
In the absence of a single global standard, companies have a multitude of regional and industry-specific options for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting. Strong ESG performance attracts savvy investors, prompting companies to adopt pre-existing standards like the GRI to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
But what is the GRI? And how can data management solutions facilitate the GRI reporting process?
What is the Global Reporting Initiative?
A historical snapshot
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) was founded in Boston in 1997, catalyzed by the 1989 Exxon Valdez incident. Heralded as the worst oil spill in U.S. history (until Deepwater Horizon in 2010), 11 million gallons of crude oil were spilled into Alaska’s Prince William Sound, devastating 1,300 miles of coastline.
Consequently, widespread public outcry prompted the GRI to create the world’s first accountability mechanism to promote responsible environmental practices for investors, businesses, and governments. In 2009, the GRI implemented the term ESG to align with growing global momentum.
For you history enthusiasts, here’s a brief overview of major GRI milestones:
- The GRI Guidelines (G1) were initially published in 2000, offering the first global framework for sustainability reporting.
- In 2001, GRI became an independent non-profit institution and relocated its Secretariat to Amsterdam, Netherlands. The Guideline’s first update resulted in the production of G2.
- The Guidelines evolved and improved over time, leading to G3 (2006) and G4 (2013).
- As sustainability reporting gained global momentum, GRI expanded its reach, establishing regional offices across continents between 2007-2019.
- In 2016, GRI made a significant shift from guidelines to establishing the groundbreaking GRI Standards—the first global standards for sustainability reporting.
Fast-forward to the present
The GRI Sustainability Reporting Standards (‘the Standards’), provide a universal language for organizations to communicate their positive and negative contributions to sustainable development. As such, the “GRI helps organizations be transparent and take responsibility for their impacts on people and the planet” (GRI, 2023). As the global gold standard for public reporting on a wide range of ESG issues, the GRI facilitates dialogue, informed decision-making, and value creation.

“GRI helps organizations be transparent and take responsibility for
their impacts on people and the planet”-The Global Reporting Initiative
It’s important to note that the GRI Standards aren’t static. Rather, they’re regularly reviewed and updated to reflect evolving sustainability challenges and stakeholder expectations. The terrain is swiftly changing. And newer additions—like the Tax (2019) and Waste (2020) Standards, and ongoing roll-out of the Sector Standards—are reflecting this.
If you’re new to the GRI Standards—or have a preference for audio-visual explanations—the following video provides a helpful overview.
Figure 1. A General Introduction to the GRI
https://youtu.be/6LkrhalWIMc
The structure of the GRI standards
The GRI Standards are a modular system, organized into three distinct areas, or series, namely:
- The Universal Standards—applicable to all types of organizations. They have been recently updated to align with international governmental expectations and include reporting on human rights and environmental due diligence.
- The Sector Standards – facilitate consistent reporting on sector-specific impacts. Each Sector Standard provides an overview of the sector's characteristics, including activities and business relationships that contribute to its impact.
- The Topic Standards – offer valuable insight to organizations regarding the material topics specific to their sector, considering the sector's significant impacts on the economy, environment, people, and even human rights.
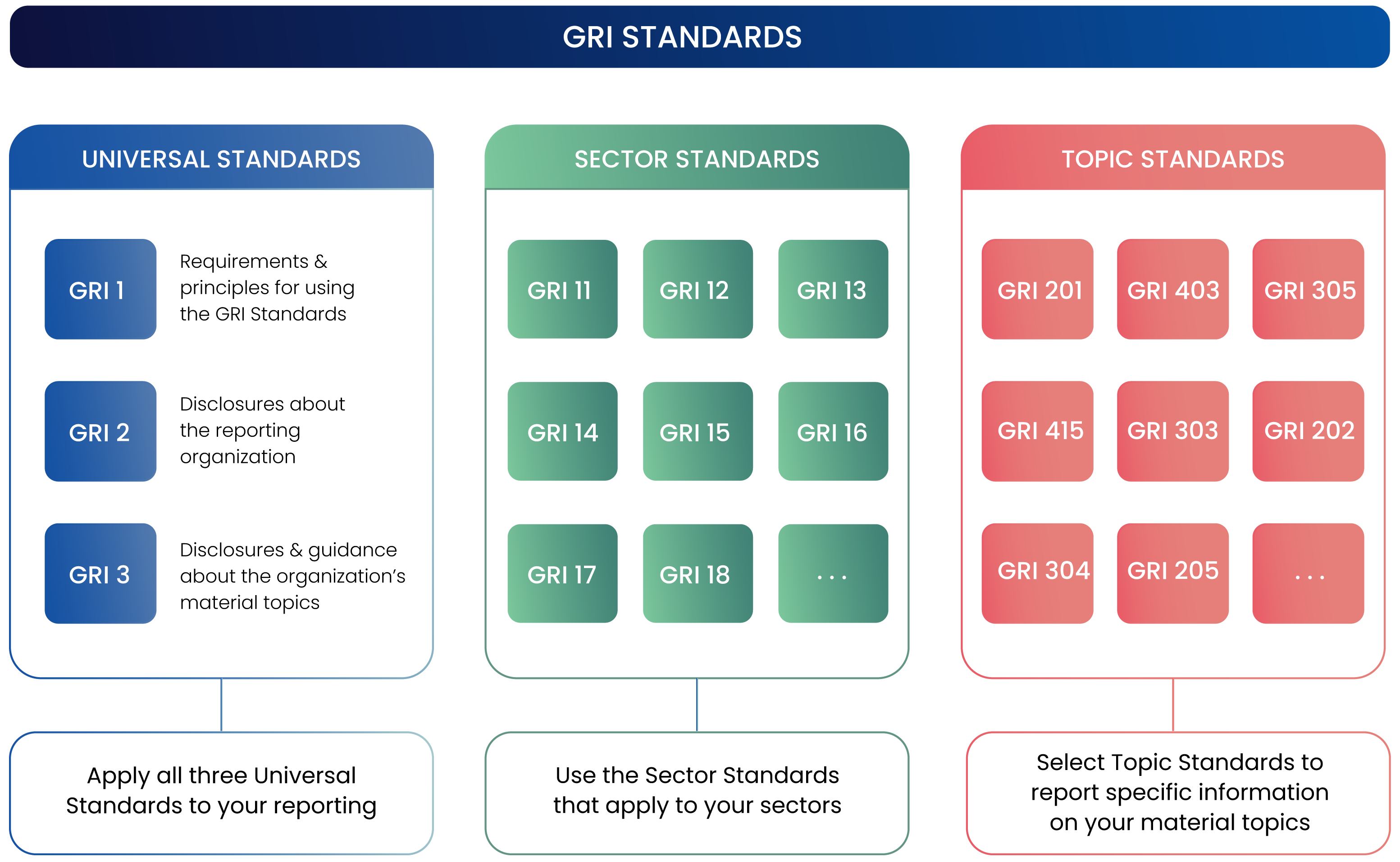
Source: "A Short Introduction to the GRI Standards," Global Reporting Initiative
Each Standard provides clear instructions on its application. They also consist of disclosures that offer a structured approach for organizations to report information about their operations and impacts. The disclosures may include requirements, specifying mandatory reporting elements, as well as recommendations for further action.
For a more granular explanation, we recommend A Short Introduction to the GRI Standards.
Why is the GRI important?
The current zeitgeist dictates that an organization’s long-term success lies in effectively managing material business issues, some of which include ESG. Yet, is this ground-breaking news?
According to our Chief ESG Innovation Officer Marie-Josée Privyk: “what's new is not the issues (for the most part), what’s new is that investors (and increasingly lenders and insurers) are explicitly considering these issues when making capital allocation decisions…”
Thus, becauseinvestors are requiring more detailed and transparent corporate ESG disclosures, annual reporting has become crucial to organizations across sectors and industries. To meet this demand, standards like the SASB, ISSB, and the GRI have proliferated.
Indeed, a growing number of organizations are embracing the GRI. According to KPMG's 2022 Global Survey of Sustainability Reporting, 78% of the world's top 250 companies and 68% of the N100 already use the GRI to report on their sustainability performance. And, with mandatory ESG reporting on the horizon, we’ll likely see heightened adoption in the years ahead.
While initial adoption might be challenging, it’s important to keep your eye on the prize. The benefits of using the GRI are numerous, and include:
- Building trust with stakeholders.
- How? By establishing sustainability commitments, setting targets, and monitoring progress.
- Promoting transparency.
- How? By enabling organizations to capture and disclose their impacts on the economy, environment and people in a comparable and reliable way.
- Unlocking new value.
- How? By understanding, managing, and disclosing their impacts, companies can enhance decision-making, mitigate risks, uncover opportunities, and strengthen stakeholder relationships.
If you’re curious to learn more about GRI and its complementarity with other reporting schemes, explore our blog post on the subject.
Now that we have an understanding of the GRI Standards and their global importance, let’s examine how SaaS solutions can facilitate their adoption.
Data management solutions for better GRI reporting
Professionals working in the ESG space know it firsthand: GRI reporting—or using any ESG standard for that matter—isn’t for the faint at heart. The challenges are numerous, spanning the usual suspects of data decentralization, an over-reliance on manual processes, and a lack of C-level buy-in to focus on material ESG issues.
Luckily, comprehensive ESG data management software (which is sometimes referred to as an ESG platform) exists to mitigate the gargantuan task at hand.
You might be thinking: fine, but how do I go about selecting the right data management tool for my organization? Where does one even begin?
And, what are some of the features and benefits that I should be aware of?
Look for a provider with deep knowledge
Wherever you are in your sustainability journey, meeting GRI reporting requirements is a complex and time-consuming endeavor. This is especially pronounced for organizations that are new to the ESG space.
Choosing a company with deep knowledge of GRI standards and methodologies is important, as this will help optimize various aspects of the reporting process.
In this vein, here are a few things to look out for:
- Do they have in-house personnel with GRI-specific expertise?
- In addition to their product offering, do they provide more general ESG-advisory services to their customers? And, are they readily available to provide this service on an ongoing basis?
In addition to deep industry knowledge, it’s important to work with a company whose offering is directly designed with the intricacies of GRI in mind. This knowledge needs to be directly reflected in the product itself—in the specific features and functionalities, and the design/user interface.
Simply put, you require a GRI deep knowledge tool.
Theory and praxis cannot be siloed here. You need to walk the talk. Hence, the next few sections will be dedicated to demystifying some of the key features and functionalities that a GRI reporting software tool should offer.
“Simply put, you require a GRI deep knowledge tool.”

Look for particular features and functionalities
GRI reporting software typically offers a range of features and functionalities designed to streamline the reporting process and ensure compliance with GRI guidelines. To deliver a comprehensive overview of your ESG performance, consider the following :
- Automated data collection: At its core, GRI reporting software automates data collection from various sources, both internal and external, such as financial records, energy consumption data, employee statistics, and supply chain information. Raw data is transformed while ensuring that reporting is accurate and nothing is double-counted or entered incorrectly.
- Data management: The software must provide tools for organizing, storing, and managing large volumes of sustainability data. Be aware of specific features such as data validation and quality checks, which are important for ensuring accuracy and precision.
- GRI reporting templates: The software should include pre-built reporting templates that are perfectly aligned with GRI standards. Embedded templates make it easier for your team to structure their sustainability reports based on the required disclosures and indicators specified by the GRI. Naturally, this will help you save time and effort come reporting season.
- Materiality assessment: The solution needs to support materiality assessments and help determine material topics. Identifying and prioritizing sustainability issues that are most significant to your organization and its stakeholders is key, as it significantly impacts your company’s ability to create value now, and into the future.
- Indicator mapping: GRI reporting software assists in mapping collected data to relevant GRI indicators. This is neat, as it helps organizations efficiently identify the appropriate metrics and indicators to measure performance in various areas such as greenhouse gas emissions, labor practices, human rights, etc.
- Performance analysis: A comprehensive software should offer analytical tools to analyze and interpret sustainability data. This enables organizations to identify trends, benchmark their performance to their peers, and track progress toward sustainability goals.
- Data visualization and reporting: Consider software that provides powerful data visualization and reporting capabilities. It’s helpful to have customizable—and comprehensive—business intelligence dashboards with visualization engines that include benchmarks, tables, charts, and graphs; this allows users to present data in a way that is informative, but also, engaging. Additionally, seek customized report builders that make reporting fast and automated, resulting in relevant narratives that are GRI-compliant.
- Stakeholder engagement: Ideally, ESG reporting software facilitates stakeholder engagement through features such as feedback management, survey tools, and interactive reporting capabilities. Look for features that facilitate transparent and inclusive stakeholder engagement throughout the reporting process.
- Audit and assurance: Embedded features to facilitate data verification and assurance processes are key for ensuring the reliability and credibility of the reported information. Given the growing importance of ESG, producing audit and investor-ready data is more imperative than ever.
The above features and functionalities are critical for streamlining your approach to GRI reporting. Yet, they are not enough.
When searching for the optimal GRI reporting software, you’ll also benefit from considering the following:
- Integration capabilities
- Scalability & flexibility
- User-centric design
Let’s turn to these now.

Consider integration
Another aspect to look out for is integration capacity: does the software offer seamless integration with existing data systems? When thinking this over, it’s helpful to consider the following:
- System compatibility: Assess whether the software is compatible with your existing systems and databases. For example, it should seamlessly integrate with other systems such as financial, HSE, HR, etc. This will ensure smooth data exchange and minimize manual data entry.
- Data import and export: Verify if the software allows for easy data import and export. It should support standard file formats for importing data from external sources, such as spreadsheets or CSV files. Similarly, it should offer options to export data for further analysis or integration with other reporting platforms if needed.
- API capabilities: Look out for software that provides application programming interface (API) capabilities. APIs allow for seamless integration between different software systems, enabling data transfer in real-time and automating processes. APIs can streamline data collection, verification, and reporting, saving time and reducing the risk of error.
- Data security: Because data security is crucial, make sure to review security measures. Ensure that the software follows industry-standard security protocols, such as encryption, access controls, and regular data backups, to protect your data from unauthorized access or loss.
Consider scalability and flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are important factors to consider for long-term sustainability reporting.
Here's what to look for:
- Scalability: Evaluate whether the software can scale with your organization's evolving needs. As your sustainability initiatives grow, you may need to handle larger data volumes, support additional sustainability metrics, and accommodate more users. The software should have the capacity to handle increased data loads and user demands without compromising performance.
- Flexibility: Assess the software's flexibility to adapt to your specific reporting requirements. Sustainability reporting needs can vary across organizations, and the software should allow for customization to meet your unique needs. Look for features that enable you to tailor the reporting templates, indicators, and data collection processes to align with your organization's sustainability goals and priorities.
- Multilingual support: If your organization operates in multiple regions or requires reporting in different languages, consider whether the software supports multilingual reporting. It should provide language localization options and comply with reporting regulations specific to different jurisdictions.
Consider user-centricity
An intuitive and user-friendly interface is crucial for successful adoption and efficient use of GRI reporting software. It can help minimize the initial (and inevitable) resistance to change, resulting in a less stressful experience overall.
Consider the following aspects:
- Ease of use: The software should have a user-friendly interface that allows for easy navigation and efficient use. And, since the reporting process involves various stakeholders with different levels of technical expertise, the software should be accessible to users of varying skill levels. Look for an intuitive design—an attractive graphical user interface doesn’t hurt—in addition to clear workflows and helpful guides or documentation.
- Training and support: Seek solutions that offer high-touch onboarding plans with dedicated customer support and ESG analysts to set your team up for success. Consider complementing this with comprehensive training materials, webinars, or online resources that can help users get up to speed quickly. Additionally, consider the availability of responsive support to address any technical issues or questions that may arise during the reporting process.
- Collaboration and user permissions: Because teamwork works, it’s important to evaluate whether the software supports easy collaboration among users within your organization. Ideally, it should enable multipleusers to work collaboratively on data collection, reporting, and review processes. Additionally, it should offer user permission controls to ensure that sensitive data is accessible only to authorized personnel.
A word of the wise: be mindful of GRI licensing
GRI takes reporting seriously and wants to make sure that its standards are used correctly. That's why they offer a specific licensing process for SaaS companies to undergo. This ensures that the software accurately incorporates the GRI Standards and adheres to best practice principles.
To this end, the GRI will conduct a thorough review of the software or digital tool to ensure that the GRI content has been implemented with the highest degree of accuracy. It will also evaluate how well the software aligns with the Standards and provide specific feedback on areas that may need some improvement.
Concluding remarks
As the worldwide industry standard for sustainability reporting, the Global Reporting Initiative has come a long way since 1997. Despite being immensely important to demonstrating your organization's dedication to sustainability and ethical business conduct, it’s not devoid of its challenges.
When it comes to GRI-compliant reporting, Novisto’s ESG data management software can reduce your load. Our platform allows you to effortlessly map your ESG data to the renowned GRI, and to easily monitor and compare your progress against your peers and competitors.
Say goodbye to complex reporting and hello to simplified ESG data management with Novisto.
Request a demo today.
