The key concepts and methodologies behind carbon accounting have a direct link to ESG—in fact, inextricably so. In an era of heightened environmental consciousness and the urgent need to combat climate change, understanding carbon accounting solutions has become imperative for organizations of all sizes.
Carbon accounting and ESG
Carbon accountingis a crucial component of ESG, particularly within the “E" (environmental) aspect. It provides a structured and data-driven approach to measuring and managing an organization's environmental impact. This is central to achieving ESG goals related to sustainability, responsibility, and long-term value creation.
Why is carbon accounting important?
The rise in carbon accounting practices reflects a changing regulatory landscape, shifting investment practices, and mounting global challenges in climate change mitigation. A wider range of stakeholders—from investors to customers—are demanding more transparency and accountability from companies about their environmental footprint.
Consequently, organizations are finding it imperative, rather than optional, to quantify their carbon emissions.
Regulatory compliance
Carbon accounting supports regulatory compliance by enabling companies to monitor, report, and reduce their carbon emissions in line with local, national, and international environmental regulations. For instance, the finalized—and highly anticipated—U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) climate change rule will require publicly listed companies to disclose their carbon emissions, including Scope 1 and Scope 2, as well as Scope 3 if they’re deemed material to the company, or if targets have been established. For more information about the upcoming SEC climate rule, explore our SEC Fact Sheet.
Access to capital
Carbon accounting enhances access to capital by attracting socially responsible investors. It demonstrates environmental responsibility, reduces long-term risks, and aligns with the growing demand for sustainable investment opportunities, making companies more appealing to investors and lenders.
By openly disclosing their carbon emissions and outlining their reduction objectives, companies assist investors in making more informed investment choices and demonstrating the potential for good ROI.
Brand reputation
Investors, customers, employees, and other stakeholders increasingly consider ESG factors when making decisions. Carbon accounting provides a quantitative, measurable metric for assessing a company's environmental performance. Meeting or exceeding stakeholder expectations regarding carbon emissions and sustainability can enhance a company's ESG reputation.
Future-proofing your business
The escalating climate crisis necessitates collective action. Companies of varying sizes across sectors and industries are realizing their responsibility in driving decarbonization, cutting emissions, and ensuring sustainability for a transition to a net-zero economy. Organizations that effectively account for and reduce their carbon emissionsare contributing to global efforts to mitigate climate change and its associated risks.
How it works
Carbon accounting involves measuring and quantifying the greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), produced by an organization, activity, or product. It encompasses tracking emissions from various sources, including:
- Energy consumption
- Transportation
- Manufacturing
Carbon accounting methods can range from simple calculations to complex models, depending on the level of accuracy and detail required. The data collected through carbon accounting is used to assess an entity's environmental impact, set emission reduction goals, and make informed decisions to mitigate climate change.
Calculating GHG emissions
Calculated greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are essential for assessing and managing the environmental impact of activities, organizations, or products. By using standardized methodologies and data collection, these emissions are quantified and expressed in terms of carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e).
A core facet of carbon accounting is determining what levels of Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions an organization is producing. Thus, the amount of Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions constitute ESG performance metricsthat companies are increasingly calculating.
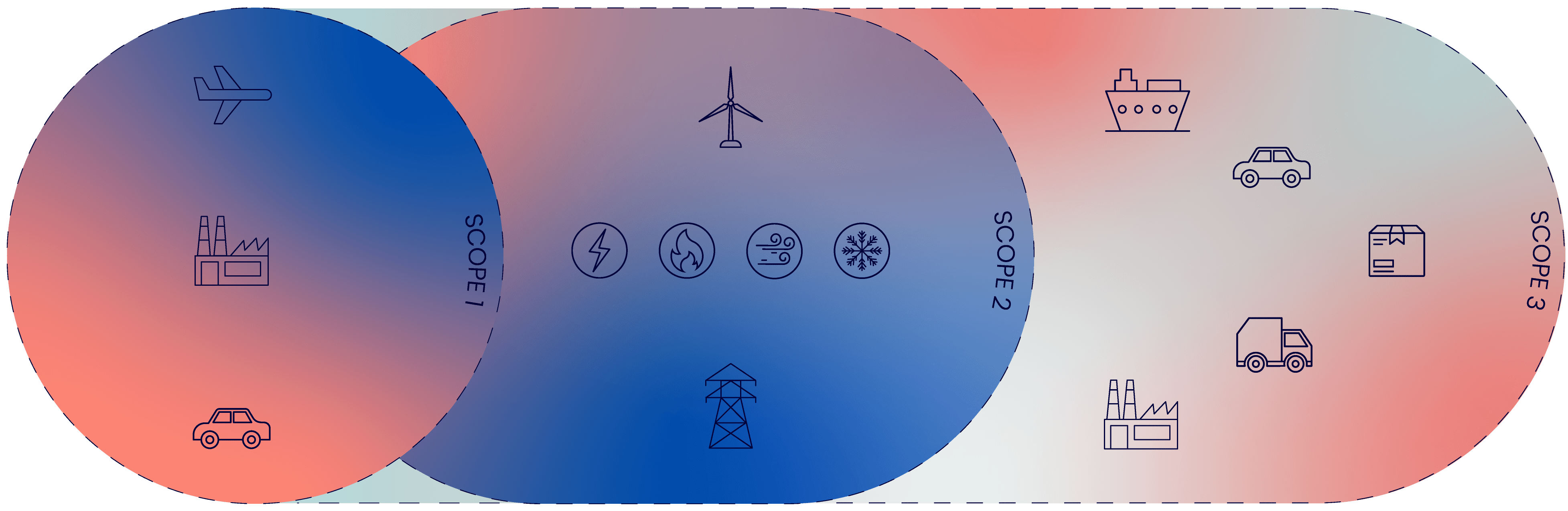
Scope 1
Scope 1 emissions are a critical component of ESG factors as they directly reflect a company's environmental impact by quantifying emissions from sources it directly controls, such as:
- On-site combustion
- Heating
- Transportation
Managing and reducing Scope 1 emissions is a key element of the "E" (environmental) in ESG, demonstrating a commitment to sustainability, environmental responsibility, and mitigating climate change.
Scope 2
Scope 2 emissions pertain to indirect greenhouse gas emissions generated from the production of purchased electricity, heating, or cooling. For inclusion in Scope 2, the energy must be produced off-site but is directly used by the reporting company.
For example, electricity that’s purchased from an energy supplier (e.g., a utility company) falls under Scope 2. When the supplier burns fossil fuels to convert them into electricity or heat, emissions are produced. Because they originate offsite, they’re categorized as “indirect”.
Scope 3
Scope 3 emissions encompass indirect emissions generated along a company's value chain, including suppliers and customers.
Addressing them reflects a commitment to assessing and reducing the broader environmental impact of an organization. It aligns with ESG's goal of promoting sustainability, responsible sourcing, and supply chain transparency, all of which contribute to a company's overall environmental responsibility and performance.
Finding a carbon accounting software that fits
To choose the best carbon accounting software for your business, start by asking a couple of questions: Are you looking for simple carbon emission tracking? Or do you require more advanced sustainability reporting? Think about your industry and the level of detail required for your operations.
It’s also vital to choose software that can grow with your business. It should be scalable to accommodate increasing data and adaptable to changing reporting needs.
Novisto’s carbon accounting solution seamlessly collects and processes emissions data from every corner of your organization and supply chain, no matter the format. This makes it the ideal platform for emissions audits and all-around business intelligence.
Contact us to learn how Novisto can help power you to net-zero.
